React Component Lifecycle Methods Cheatsheet 📄
2019, Nov 24
| React Component Lifecycle Cheatsheet |
|---|
| React Component Lifecycle Methods Cheatsheet |
| React Component Lifecycle Hooks Cheatsheet |
Each component in React has a lifecycle which you can monitor and manipulate.
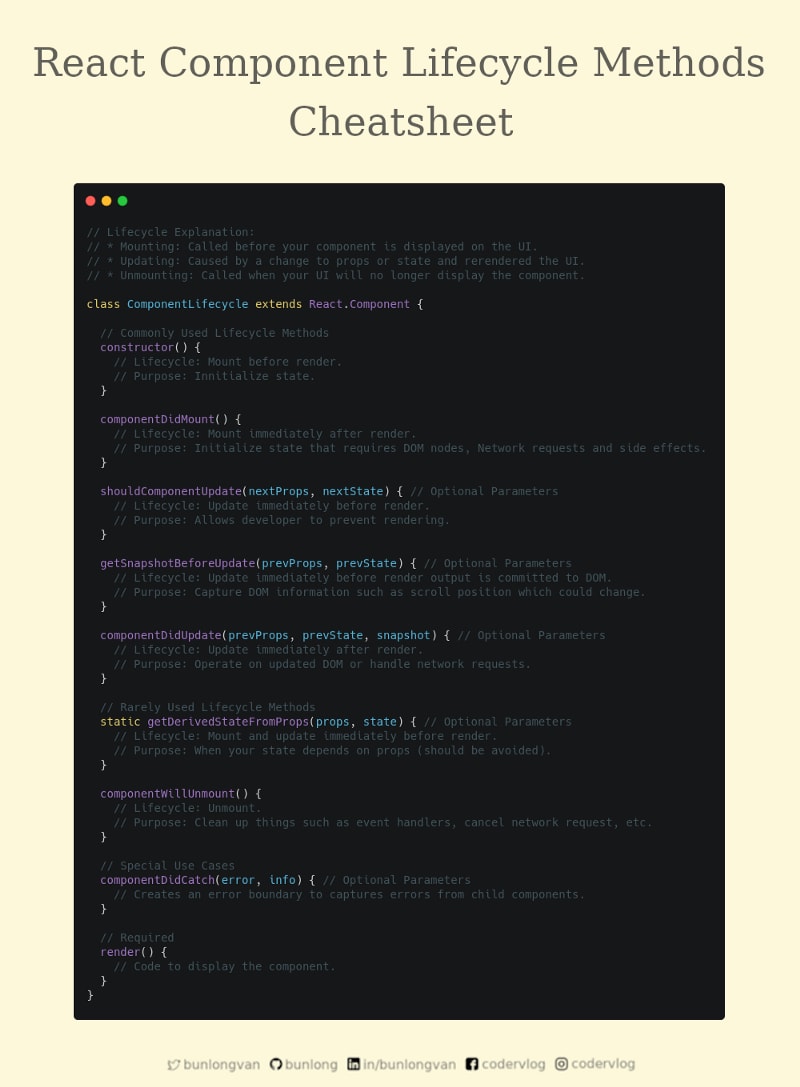
Lifecycle Explanation:
- Mounting: Called before your component is displayed on the UI.
- Updating: Caused by a change to props or state and rerendered the UI.
- Unmounting: Called when your UI will no longer display the component.
Mounting
constructor
- Lifecycle: Mount immediately before render.
- Purpose: Initialize state.
// Commonly Used Lifecycle Methods
constructor() {
}
componentDidMount
- Lifecycle: Mount immediately after render.
- Purpose: Initialize state that requires DOM nodes, Network requests and side effects.
componentDidMount() {
}
Updating
shouldComponentUpdate
- Lifecycle: Update immediately before render.
- Purpose: Allows developer to prevent rendering.
shouldComponentUpdate(nextProps, nextState) { // Optional Parameters
}
render
Code to display the component.
// Required
render() {
}
getSnapshotBeforeUpdate
- Lifecycle: Update immediately before render output is committed to DOM.
- Purpose: Capture DOM information such as scroll position which could change.
getSnapshotBeforeUpdate(prevProps, prevState) { // Optional Parameters
}
componentDidUpdate
- Lifecycle: Update immediately after render.
- Purpose: Operate on updated DOM or handle network requests.
componentDidUpdate(prevProps, prevState, snapshot) { // Optional Parameters
}
Mounting & Updating
getDerivedStateFromProps
- Lifecycle: Mount and update immediately before render.
- Purpose: When your state depends on props (should be avoided).
// Rarely Used Lifecycle Methods
static getDerivedStateFromProps(props, state) { // Optional Parameters
}
Unmounting
componentWillUnmount
- Lifecycle: Unmount.
- Purpose: Clean up things such as event handlers, cancel network request, etc.
componentWillUnmount() {
}
Other Methods
componentDidCatch
Creates an error boundary to captures errors from child components.
// Special Use Cases
componentDidCatch(error, info) { // Optional Parameters
}
References
Thanks for reading ❤
Say Hello! Twitter | Github | LinkedIn | Facebook | Instagram
Like ❤️
